pygmt.Figure.plot¶
-
Figure.plot(x=None, y=None, data=None, sizes=None, direction=None, **kwargs)¶ Plot lines, polygons, and symbols in 2-D.
Takes a matrix, (x,y) pairs, or a file name as input and plots lines, polygons, or symbols at those locations on a map.
Must provide either data or x and y.
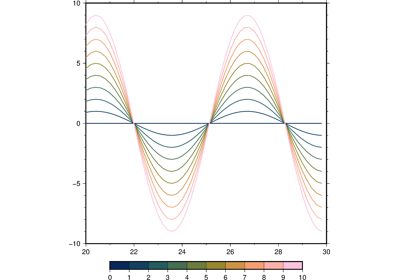
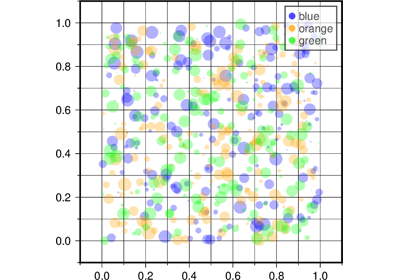
If providing data through x and y, color can be a 1d array that will be mapped to a colormap.
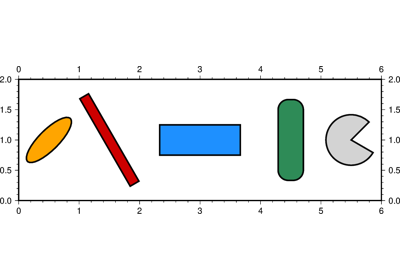
If a symbol is selected and no symbol size given, then plot will interpret the third column of the input data as symbol size. Symbols whose size is <= 0 are skipped. If no symbols are specified then the symbol code (see style below) must be present as last column in the input. If style is not used, a line connecting the data points will be drawn instead. To explicitly close polygons, use close. Select a fill with color. If color is set, pen will control whether the polygon outline is drawn or not. If a symbol is selected, color and pen determines the fill and outline/no outline, respectively.
Full option list at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/plot.html
Aliases:
A = straight_line
B = frame
C = cmap
D = offset
E = error_bar
F = connection
G = color
I = intensity
J = projection
L = close
N = no_clip
R = region
S = style
U = timestamp
V = verbose
W = pen
X = xshift
Y = yshift
Z = zvalue
c = panel
i = columns
l = label
p = perspective
t = transparency
- Parameters
x/y (float or 1d arrays) – The x and y coordinates, or arrays of x and y coordinates of the data points
data (str or 2d array) – Either a data file name or a 2d numpy array with the tabular data. Use option columns (i) to choose which columns are x, y, color, and size, respectively.
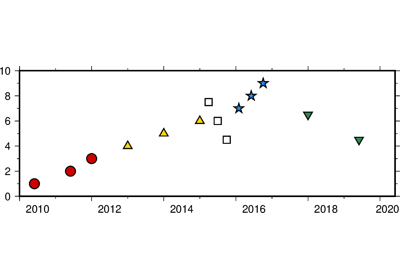
sizes (1d array) – The sizes of the data points in units specified in style (S). Only valid if using x and y.
direction (list of two 1d arrays) – If plotting vectors (using
style='V'orstyle='v'), then should be a list of two 1d arrays with the vector directions. These can be angle and length, azimuth and length, or x and y components, depending on the style options chosen.projection (str) – Required if this is the first plot command. Select map projection.
region (str or list) – Required if this is the first plot command.
'xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax[+r][+uunit]'. Specify the region of interest.straight_line (bool or str) –
[m|p|x|y]. By default, geographic line segments are drawn as great circle arcs. To draw them as straight lines, use straight_line. Alternatively, add m to draw the line by first following a meridian, then a parallel. Or append p to start following a parallel, then a meridian. (This can be practical to draw a line along parallels, for example). For Cartesian data, points are simply connected, unless you append x or y to draw stair-case curves that whose first move is along x or y, respectively.frame (str or list) – Set map boundary frame and axes attributes.
cmap (str) – File name of a CPT file or
C='color1,color2[,color3,...]'to build a linear continuous CPT from those colors automatically.offset (str) –
dx/dy. Offset the plot symbol or line locations by the given amounts dx/dy [Default is no offset]. If dy is not given it is set equal to dx.error_bar (bool or str) –
[x|y|X|Y][+a][+cl|f][+n][+wcap][+ppen]. Draw symmetrical error bars. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/plot.html#e.connection (str) –
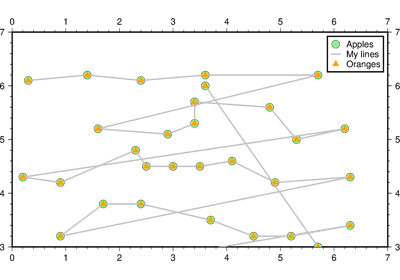
[c|n|r][a|f|s|r|refpoint]. Alter the way points are connected (by specifying a scheme) and data are grouped (by specifying a method). Append one of three line connection schemes:c : Draw continuous line segments for each group [Default].
r : Draw line segments from a reference point reset for each group.
n : Draw networks of line segments between all points in each group.
Optionally, append the one of four segmentation methods to define the group:
a : Ignore all segment headers, i.e., let all points belong to a single group, and set group reference point to the very first point of the first file.
f : Consider all data in each file to be a single separate group and reset the group reference point to the first point of each group.
s : Segment headers are honored so each segment is a group; the group reference point is reset to the first point of each incoming segment [Default].
r : Same as s, but the group reference point is reset after each record to the previous point (this method is only available with the
connection='r'scheme).
Instead of the codes a**|**f**|**s**|**r you may append the coordinates of a refpoint which will serve as a fixed external reference point for all groups.
color (str) – Select color or pattern for filling of symbols or polygons. Default is no fill.
intensity (float or bool) – Provide an intens value (nominally in the -1 to +1 range) to modulate the fill color by simulating illumination [None]. If using
intensity=True, we will instead read intens from the first data column after the symbol parameters (if given).close (str) –
[+b|d|D][+xl|r|x0][+yl|r|y0][+ppen]. Force closed polygons. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/plot.html#l.no_clip (bool or str) –
'[c|r]'. Do NOT clip symbols that fall outside map border [Default plots points whose coordinates are strictly inside the map border only]. The option does not apply to lines and polygons which are always clipped to the map region. For periodic (360-longitude) maps we must plot all symbols twice in case they are clipped by the repeating boundary.no_clip=Truewill turn off clipping and not plot repeating symbols. Useno_clip="r"to turn off clipping but retain the plotting of such repeating symbols, or useno_clip="c"to retain clipping but turn off plotting of repeating symbols.style (str) – Plot symbols (including vectors, pie slices, fronts, decorated or quoted lines).
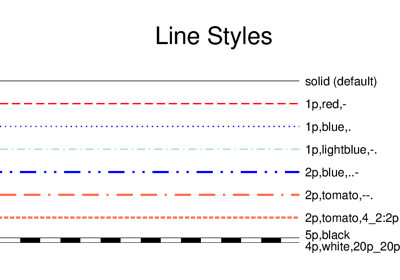
pen (str) – Set pen attributes for lines or the outline of symbols.
verbose (str) –
Select verbosity level [Default is w], which modulates the messages written to stderr. Choose among 7 levels of verbosity:
q - Quiet, not even fatal error messages are produced
e - Error messages only
w - Warnings [Default]
t - Timings (report runtimes for time-intensive algorthms);
i - Informational messages (same as “verbose=True”)
c - Compatibility warnings
d - Debugging messages
xshift (str) –
[a|c|f|r][xshift]. Shift plot origin in x-direction.yshift (str) –
[a|c|f|r][yshift]. Shift plot origin in y-direction. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/gmt.html#xy-full.zvalue (str) –
value|file. Instead of specifying a symbol or polygon fill and outline color via color and pen, give both a value via zvalue and a color lookup table via cmap. Alternatively, give the name of a file with one z-value (read from the last column) for each polygon in the input data. To apply it to the fill color, usecolor='+z'. To apply it to the pen color, append +z to pen.panel (int or list) – [row,col|index]. Used to advance to the selected subplot panel. Only allowed when in subplot mode. Available to all plot modules. If no arguments are given then we advance to the next panel in the selected order. If no panel is given and we just entered subplot mode then the first panel (top, left) is selected. Instead of row, col you may give the one-dimensional index which depends on the order you set via autolabel when the subplot was defined. Note: row, col, and index all start at 0.
columns (str or 1d array) – Choose which columns are x, y, color, and size, respectively if input is provided via data. E.g.
columns = [0, 1]orcolumns = '0,1'if the x values are stored in the first column and y values in the second one. Note: zero-based indexing is used.label (str) – Add a legend entry for the symbol or line being plotted.
perspective (list or str) –
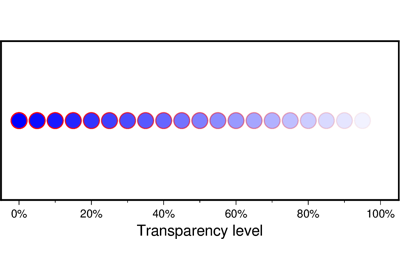
'[x|y|z]azim[/elev[/zlevel]][+wlon0/lat0[/z0]][+vx0/y0]'. Select perspective view and set the azimuth and elevation angle of the viewpoint. Default is [180, 90]. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/gmt.html#perspective-full.transparency (float) – Set transparency level, in [0-100] percent range. Default is 0, i.e., opaque. Only visible when PDF or raster format output is selected. Only the PNG format selection adds a transparency layer in the image (for further processing). transparency can also be a 1d array to set varying transparency for symbols.